How Rsa Key Generation Exponent Secret
- How Rsa Key Generation Exponent Secret Code
- How Rsa Key Generation Exponent Secret 1
- Rsa Key Generation Windows
- Cisco Rsa Key Generation
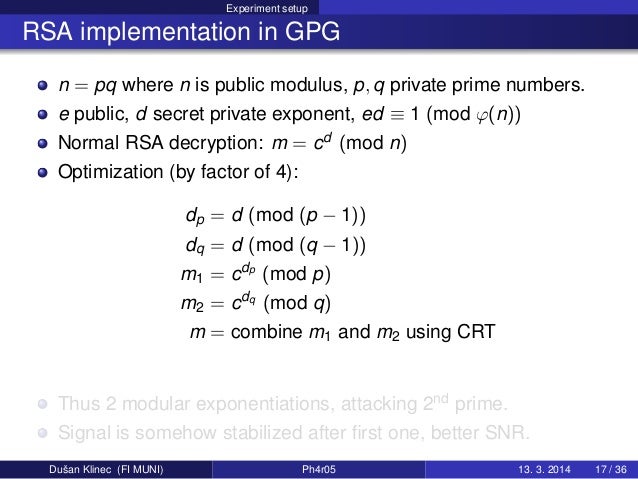
Jul 16, 2019 RSA involves a public key and a private key. The public key should be known by everyone and is used for encrypting messages. Messages encrypted with the public key can only be decrypted in a reasonable amount of time using the private key. In RSA, this asymmetry is based on the practical difficulty of factoring the product of two large prime. Online RSA key generation: RSA (Rivest, Shamir and Adleman) is an asymmetric (or public-key) cryptosystem which is often used in combination with a symmetric cryptosystem such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard). It holds the entire RSA key-pair structure, along with several additional parameters: 2048-bit modulus n, 24-bit public exponent e, 2048-bit secret exponent d, first factor p, second factor q, and 3 other integers from the RSA internal data structure. How to generate public/private key in C#. Asymmetric cryptography also known as public-key encryption uses a public/private key pair to encrypt and decrypt data. In.NET, the RSACryptoServiceProvider and DSACryptoServiceProvider classes are used for asymmetric encryption. Nov 04, 2014 Meet Eddie Woo, the maths teacher you wish you’d had in high school Australian Story - Duration: 28:09. ABC News In-depth Recommended for you. ROM THE SET of all key pairs for the RSA public- key cryptosystem 5, some key pairs have properties that can be exploited by various cryptanalytic attacks. Some attacks exploit weaknesses in the modulus, and others exploit weaknesses in the public exponent or the secret exponent.
-->Creates a new key, stores it, then returns key parameters and attributes to the client.
The create key operation can be used to create any key type in Azure Key Vault. If the named key already exists, Azure Key Vault creates a new version of the key. It requires the keys/create permission.
URI Parameters
| Name | In | Required | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| path | True |
| The name for the new key. The system will generate the version name for the new key. Regex pattern: | |
vaultBaseUrl | path | True |
| The vault name, for example https://myvault.vault.azure.net. |
| query | True |
| Client API version. |
Request Body
| Name | Required | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| attributes | The attributes of a key managed by the key vault service. | ||
| crv | Elliptic curve name. For valid values, see JsonWebKeyCurveName. | ||
| key_ops |
| JSON web key operations. For more information, see JsonWebKeyOperation. | |
| key_size |
| The key size in bits. For example: 2048, 3072, or 4096 for RSA. | |
| kty | True | The type of key to create. For valid values, see JsonWebKeyType. | |
| tags |
| Application specific metadata in the form of key-value pairs. |
Responses
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 200 OK | A key bundle containing the result of the create key request. | |
| Other Status Codes | Key Vault error response describing why the operation failed. |
Examples
Create key
Sample Request
Definitions
| DeletionRecoveryLevel | Reflects the deletion recovery level currently in effect for keys in the current vault. If it contains 'Purgeable' the key can be permanently deleted by a privileged user; otherwise, only the system can purge the key, at the end of the retention interval. |
| Error | The key vault server error. |
| JsonWebKey | As of http://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-jose-json-web-key-18 |
| JsonWebKeyCurveName | Elliptic curve name. For valid values, see JsonWebKeyCurveName. |
| JsonWebKeyType | JsonWebKey Key Type (kty), as defined in https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-jose-json-web-algorithms-40. |
| KeyAttributes | The attributes of a key managed by the key vault service. |
| KeyBundle | A KeyBundle consisting of a WebKey plus its attributes. |
| KeyCreateParameters | The key create parameters. |
| KeyVaultError | The key vault error exception. |
DeletionRecoveryLevel
Reflects the deletion recovery level currently in effect for keys in the current vault. If it contains 'Purgeable' the key can be permanently deleted by a privileged user; otherwise, only the system can purge the key, at the end of the retention interval.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Purgeable |
| |
| Recoverable |
| |
| Recoverable+ProtectedSubscription |
| |
| Recoverable+Purgeable |
|
Error
The key vault server error.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| code |
| The error code. |
| innererror | The key vault server error. | |
| message |
| The error message. |
JsonWebKey
As of http://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-jose-json-web-key-18
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| crv | Elliptic curve name. For valid values, see JsonWebKeyCurveName. | |
| d |
| RSA private exponent, or the D component of an EC private key. |
| dp |
| RSA private key parameter. |
| dq |
| RSA private key parameter. |
| e |
| RSA public exponent. |
| k |
| Symmetric key. |
| key_hsm |
| HSM Token, used with 'Bring Your Own Key'. |
| key_ops |
| Supported key operations. |
| kid |
| Key identifier. |
| kty | JsonWebKey Key Type (kty), as defined in https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-jose-json-web-algorithms-40. | |
| n |
| RSA modulus. |
| p |
| RSA secret prime. |
| q |
| RSA secret prime, with p < q. |
| qi |
| RSA private key parameter. |
| x |
| X component of an EC public key. |
| y |
| Y component of an EC public key. |
JsonWebKeyCurveName
Elliptic curve name. For valid values, see JsonWebKeyCurveName.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| P-256 |
| The NIST P-256 elliptic curve, AKA SECG curve SECP256R1. |
| P-256K |
| The SECG SECP256K1 elliptic curve. |
| P-384 |
| The NIST P-384 elliptic curve, AKA SECG curve SECP384R1. |
| P-521 |
| The NIST P-521 elliptic curve, AKA SECG curve SECP521R1. Download adobe acrobat reader 7.0 professional full crack. |
JsonWebKeyType
JsonWebKey Key Type (kty), as defined in https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-jose-json-web-algorithms-40.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| EC |
| Elliptic Curve. |
| EC-HSM |
| Elliptic Curve with a private key which is not exportable from the HSM. |
| RSA |
| RSA (https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3447) |
| RSA-HSM |
| RSA with a private key which is not exportable from the HSM. |
| oct |
| Octet sequence (used to represent symmetric keys) |
KeyAttributes
The attributes of a key managed by the key vault service.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| created |
| Creation time in UTC. |
| enabled |
| Determines whether the object is enabled. |
| exp |
| Expiry date in UTC. |
| nbf |
| Not before date in UTC. |
| recoveryLevel | Reflects the deletion recovery level currently in effect for keys in the current vault. If it contains 'Purgeable' the key can be permanently deleted by a privileged user; otherwise, only the system can purge the key, at the end of the retention interval. | |
| updated |
| Last updated time in UTC. |
KeyBundle
A KeyBundle consisting of a WebKey plus its attributes.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| attributes | The key management attributes. | |
| key | The Json web key. | |
| managed |
| True if the key's lifetime is managed by key vault. If this is a key backing a certificate, then managed will be true. |
| tags |
| Application specific metadata in the form of key-value pairs. |
KeyCreateParameters
The key create parameters.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| attributes | The attributes of a key managed by the key vault service. | |
| crv | Elliptic curve name. For valid values, see JsonWebKeyCurveName. | |
| key_ops |
| JSON web key operations. For more information, see JsonWebKeyOperation. |
| key_size |
| The key size in bits. For example: 2048, 3072, or 4096 for RSA. |
| kty | The type of key to create. For valid values, see JsonWebKeyType. | |
| tags |
| Application specific metadata in the form of key-value pairs. |
KeyVaultError
The key vault error exception.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| error | /license-key-generator-for-pc-games-online.html. The key vault server error. |
How Rsa Key Generation Exponent Secret Code
-->Creating and managing keys is an important part of the cryptographic process. Symmetric algorithms require the creation of a key and an initialization vector (IV). The key must be kept secret from anyone who should not decrypt your data. The IV does not have to be secret, but should be changed for each session. Asymmetric algorithms require the creation of a public key and a private key. The public key can be made public to anyone, while the private key must known only by the party who will decrypt the data encrypted with the public key. This section describes how to generate and manage keys for both symmetric and asymmetric algorithms.
Symmetric Keys
The symmetric encryption classes supplied by the .NET Framework require a key and a new initialization vector (IV) to encrypt and decrypt data. Whenever you create a new instance of one of the managed symmetric cryptographic classes using the parameterless constructor, a new key and IV are automatically created. Anyone that you allow to decrypt your data must possess the same key and IV and use the same algorithm. Generally, a new key and IV should be created for every session, and neither the key nor IV should be stored for use in a later session.
To communicate a symmetric key and IV to a remote party, you would usually encrypt the symmetric key by using asymmetric encryption. Sending the key across an insecure network without encrypting it is unsafe, because anyone who intercepts the key and IV can then decrypt your data. For more information about exchanging data by using encryption, see Creating a Cryptographic Scheme.

The following example shows the creation of a new instance of the TripleDESCryptoServiceProvider class that implements the TripleDES algorithm.
When the previous code is executed, a new key and IV are generated and placed in the Key and IV properties, respectively.
Sometimes you might need to generate multiple keys. In this situation, you can create a new instance of a class that implements a symmetric algorithm and then create a new key and IV by calling the GenerateKey and GenerateIV methods. The following code example illustrates how to create new keys and IVs after a new instance of the symmetric cryptographic class has been made.
When the previous code is executed, a key and IV are generated when the new instance of TripleDESCryptoServiceProvider is made. Another key and IV are created when the GenerateKey and GenerateIV methods are called.
Asymmetric Keys
The .NET Framework provides the RSACryptoServiceProvider and DSACryptoServiceProvider classes for asymmetric encryption. These classes create a public/private key pair when you use the parameterless constructor to create a new instance. Asymmetric keys can be either stored for use in multiple sessions or generated for one session only. While the public key can be made generally available, the private key should be closely guarded.
A public/private key pair is generated whenever a new instance of an asymmetric algorithm class is created. After a new instance of the class is created, the key information can be extracted using one of two methods:
How Rsa Key Generation Exponent Secret 1
The ToXmlString method, which returns an XML representation of the key information.
The ExportParameters method, which returns an RSAParameters structure that holds the key information.
Both methods accept a Boolean value that indicates whether to return only the public key information or to return both the public-key and the private-key information. An RSACryptoServiceProvider class can be initialized to the value of an RSAParameters structure by using the ImportParameters method.
Asymmetric private keys should never be stored verbatim or in plain text on the local computer. If you need to store a private key, you should use a key container. For more on how to store a private key in a key container, see How to: Store Asymmetric Keys in a Key Container.
Rsa Key Generation Windows
The following code example creates a new instance of the RSACryptoServiceProvider class, creating a public/private key pair, and saves the public key information to an RSAParameters structure.