Generate Git Ssh Key Ubuntu
- Generate Git Ssh Key Ubuntu Windows 7
- Generate Git Ssh Key Ubuntu Download
- Generate Git Ssh Key Ubuntu Free
Jul 09, 2018 “How to Add an SSH Public Key to GitHub from an Ubuntu 18.04 LTS System” covers the entire process of creating an SSH key pair on an Ubuntu 18.04 LTS system and adding the public key to. Jun 22, 2012 SSH keys provide a more secure way of logging into a virtual private server with SSH than using a password alone. With SSH keys, users can log into a server without a password. This tutorial explains how to generate, use, and upload an SSH Key Pair.
When you work with a Git repository, your project may be actively modified by a lot of people. Some of them may not be trustworthy as they may be new employees or something like that. In this case, if they need to do git pull in the server to update the changes of a commit in your production server, you may not want that everybody knows the password of the repository. Another case where you don't want to provide the password of the repository everytime you do git pull or git clone, are automatized deployments.
That's why the the 'deployment keys' feature exist in Gitlab, A deploy key is an SSH key that is stored on your server and grants access to a single Gitlab repository. This key is attached directly to the repository instead of to a personal user account. In this article, we'll show you step by step how you can automatize the deployment process of your project hosted on Gitlab.
1. Find or create an SSH Key for your server
The first thing that you need to do is to verify if your server has already a public key created in the .ssh directory of the user in the server, so start a SSH session to your server and type the following command:
This will automatically search in the folder of your user that in our case is /home/vagrant/.ssh, if the output of the command shows a string that starts with ssh-rsa, then you already have an SSH Key that you can use to add to your repository, so you can skip to the step 2. If instead, you get the output : cat: ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub: No such file or directory, then you will need to create an SSH Key first. You can create a SSH Key in Ubuntu via SSH with the following command (navigate to the .ssh directory first and type):
To make the process easy, we won't add a Keyphrase for the SSH Key, so as mentioned in the creation wizard just press enter to don't use a keyphrase:
As shown in the image, we no have the id_rsa and id_rsa.pub file in our .ssh directory. This key works as a 'pass' that allows to clone/pull your project in the current server, till this point it doesn't do anything, so you will need to follow the other steps.
2. Configure SSH client to find your GitLab private SSH in the server
As next step you need to establish that, when cloning from Gitlab, the deployment key should be used as authentication instead of an username and a password. For this you need to ensure that ssh-agent is enabled by running the following command:
Then you can proceed to add your key to the SSH registry using the following command:
To retain these settings you'll need to save them to a configuration file. Normally on OpenSSH clients you can configure this in the ~/.ssh/config file. If the file doesn't exist, you can create it:
And register your key in the file. In this tutorial we are adding a single SSH Key from the Gitlab website (non self hosted version), so our config file content will be:
As you may have multiple projects in one server or a project that uses different repositories that need to be updated, you can without a problem implement multiple SSH Keys in the same file following the notation:
3. Add the Server Key as a deployment key in your Repository configuration
Now you need the public key of your server (created in step 1), in this step you are saying to Gitlab 'Hey, if someone uses this SSH Key to clone, allow him to do it'. You can get the content of the public file using a text editor via SFTP, or just by printing the output of the file with SSH using the following command:
This would output in our case the content of the public key:
Keep that long string in the clipboard as you will need it to paste it in Gitlab. As next acccess the Settings of your Repository in Gitlab, in our case as we are using the non self hosted version of Gitlab the configuration for the Deploy Keys is in https://gitlab.com/<username>/<repository-name>/settings/repository. The menu to add a new deploy key looks like this:
Here you would only need to add the content of the id_rsa.pub file, provide a title and decide wheter the server can be used to push changes as well or not (normally unchecked as it is production). Once the key is added in your repository, you should be able now to clone/pull your repository in the deployment server.
4. Clone and pull repository to test
As final step, to verify if everything went right you can clone your repository to see if the credentials of the repository are requested or not, in case it does, please read the tutorial again and check what you did wrong. Otherwise, you will be able to clone your project using the following command:
Note
Remember to clone via SSH, not HTTPS, otherwise you may obviously be asked for the credentials.
By doing this you may have noticed that you didn't have to input your Gitlab username nor password thanks to the deployment key!
Hindi typing master free download full version for windows 7 ultimate. Happy coding !
SSH keys are a necessity for Python development when you are working withGit, connecting to remote servers and automating yourdeployments. Let's walk through how to generate SSHkey pairs, which contain both a public and a private key within a singlepair, on Ubuntu Linux.
Generating the Public and Private Keys
Open up a new terminal window in Ubuntu like we see in the followingscreenshot.
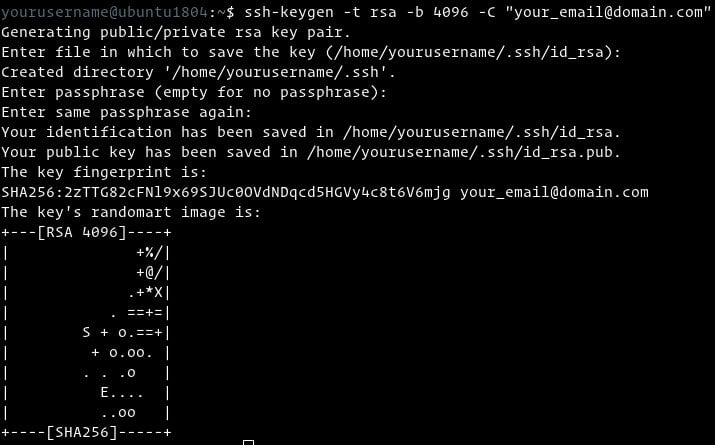
Ssh-keygen generate dsa key. The ssh-keygen command provides an interactive command line interface forgenerating both the public and private keys. Invoke ssh-keygen with thefollowing -t and -b arguments to ensure we get a 4096 bit RSA key.Optionally, you can also specify your email address with -C (otherwiseone will be generated off your current Linux account):
(Note: the -o option was introduced in 2014; if this command fails for you, simply remove the -o option)
Generate Git Ssh Key Ubuntu Windows 7
The first prompt you will see asks where to save the key. However, there areactually two files that will be generated: the public key and the privatekey.
This prompt refers to the private key and whatever you enter will alsogenerate a second file for the public key that has the same name and .pubappended.
If you already have a key, you should specify a new filename. I use manySSH keys so I typically name them 'test-deploy', 'prod-deploy', 'ci-server'along with a unique project name. Naming is one of those hard computerscience problems, so take some time to come up with a system that works foryou and the development team you work with!
Next you will see a prompt for an optional passphrase:
Generate Git Ssh Key Ubuntu Download
Whether or not you want a passphrase depends on how you will use the key.The system will ask you for the passphrase whenever you use the SSH keyso it is more secure.However, if you are automating deployments with acontinuous integration server likeJenkins then you will not want a passphrase.
Generate Git Ssh Key Ubuntu Free
Be aware that it is impossible to recover a passphrase if it is lost. Keepthat passphrase safe and secure because otherwise a completely new key wouldhave to be generated.
Enter the passphrase (or just press enter to not have a passphrase) twice.You'll see some output like the following:
Your SSH key is now generated and ready to use!
What now?
Now that you have your public and private keys, I recommend settingup a Python development environment withone of the following tutorials so you can start coding:
Additional ssh-keygen command resources:
Questions? Contact me via Twitter@fullstackpythonor @mattmakai. I'm also on GitHub withthe username mattmakai.
See something wrong in this post? Forkthis page's source on GitHuband submit a pull request.